isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer
Source code on GitHub.
Quickstart
Set Up Development Environment
Set up your development environment by following the instructions in getting started.
Clone
isaac_ros_commonunder${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src.cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src && \ git clone -b release-3.2 https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_common.git isaac_ros_common
(Optional) Install dependencies for any sensors you want to use by following the sensor-specific guides.
Note
We strongly recommend installing all sensor dependencies before starting any quickstarts. Some sensor dependencies require restarting the Isaac ROS Dev container during installation, which will interrupt the quickstart process.
Download Quickstart Assets
Download quickstart data from NGC:
Make sure required libraries are installed.
sudo apt-get install -y curl jq tar
Then, run these commands to download the asset from NGC:
NGC_ORG="nvidia" NGC_TEAM="isaac" PACKAGE_NAME="isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer" NGC_RESOURCE="isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer_assets" NGC_FILENAME="quickstart.tar.gz" MAJOR_VERSION=3 MINOR_VERSION=2 VERSION_REQ_URL="https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/api/resources/versions?orgName=$NGC_ORG&teamName=$NGC_TEAM&name=$NGC_RESOURCE&isPublic=true&pageNumber=0&pageSize=100&sortOrder=CREATED_DATE_DESC" AVAILABLE_VERSIONS=$(curl -s \ -H "Accept: application/json" "$VERSION_REQ_URL") LATEST_VERSION_ID=$(echo $AVAILABLE_VERSIONS | jq -r " .recipeVersions[] | .versionId as \$v | \$v | select(test(\"^\\\\d+\\\\.\\\\d+\\\\.\\\\d+$\")) | split(\".\") | {major: .[0]|tonumber, minor: .[1]|tonumber, patch: .[2]|tonumber} | select(.major == $MAJOR_VERSION and .minor <= $MINOR_VERSION) | \$v " | sort -V | tail -n 1 ) if [ -z "$LATEST_VERSION_ID" ]; then echo "No corresponding version found for Isaac ROS $MAJOR_VERSION.$MINOR_VERSION" echo "Found versions:" echo $AVAILABLE_VERSIONS | jq -r '.recipeVersions[].versionId' else mkdir -p ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets && \ FILE_REQ_URL="https://api.ngc.nvidia.com/v2/resources/$NGC_ORG/$NGC_TEAM/$NGC_RESOURCE/\ versions/$LATEST_VERSION_ID/files/$NGC_FILENAME" && \ curl -LO --request GET "${FILE_REQ_URL}" && \ tar -xf ${NGC_FILENAME} -C ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets && \ rm ${NGC_FILENAME} fi
Build isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer
Launch the Docker container using the
run_dev.shscript:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh
Install the prebuilt Debian package:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y ros-humble-isaac-ros-occupancy-grid-localizer
Clone this repository under
${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src && \ git clone -b release-3.2 https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_map_localization.git isaac_ros_map_localization
Launch the Docker container using the
run_dev.shscript:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh
Use
rosdepto install the package’s dependencies:sudo apt-get update
rosdep update && rosdep install --from-paths ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_map_localization/isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer --ignore-src -y
Build the package from source:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS} && \ colcon build --symlink-install --packages-up-to isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer --base-paths ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_map_localization/isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer
Source the ROS workspace:
Note
Make sure to repeat this step in every terminal created inside the Docker container.
Since this package was built from source, the enclosing workspace must be sourced for ROS to be able to find the package’s contents.
source install/setup.bash
Run Launch File
Continuing inside the Docker container,
rviz2:rviz2 -d $(ros2 pkg prefix isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer --share)/rviz/quickstart.rviz
Create another terminal in the Docker container using the
run_dev.shscript:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh
Run the launch file to spin up a demo of this package:
ros2 launch isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer_quickstart.launch.py
Create another terminal in the Docker container using the
run_dev.shscript:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh
Run the rosbag:
ros2 bag play -l ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer/rosbags/flatscan
- Create another terminal in the Docker container using the
run_dev.shscript:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh
Trigger the localization using a command line service call:
ros2 service call trigger_grid_search_localization std_srvs/srv/Empty {}
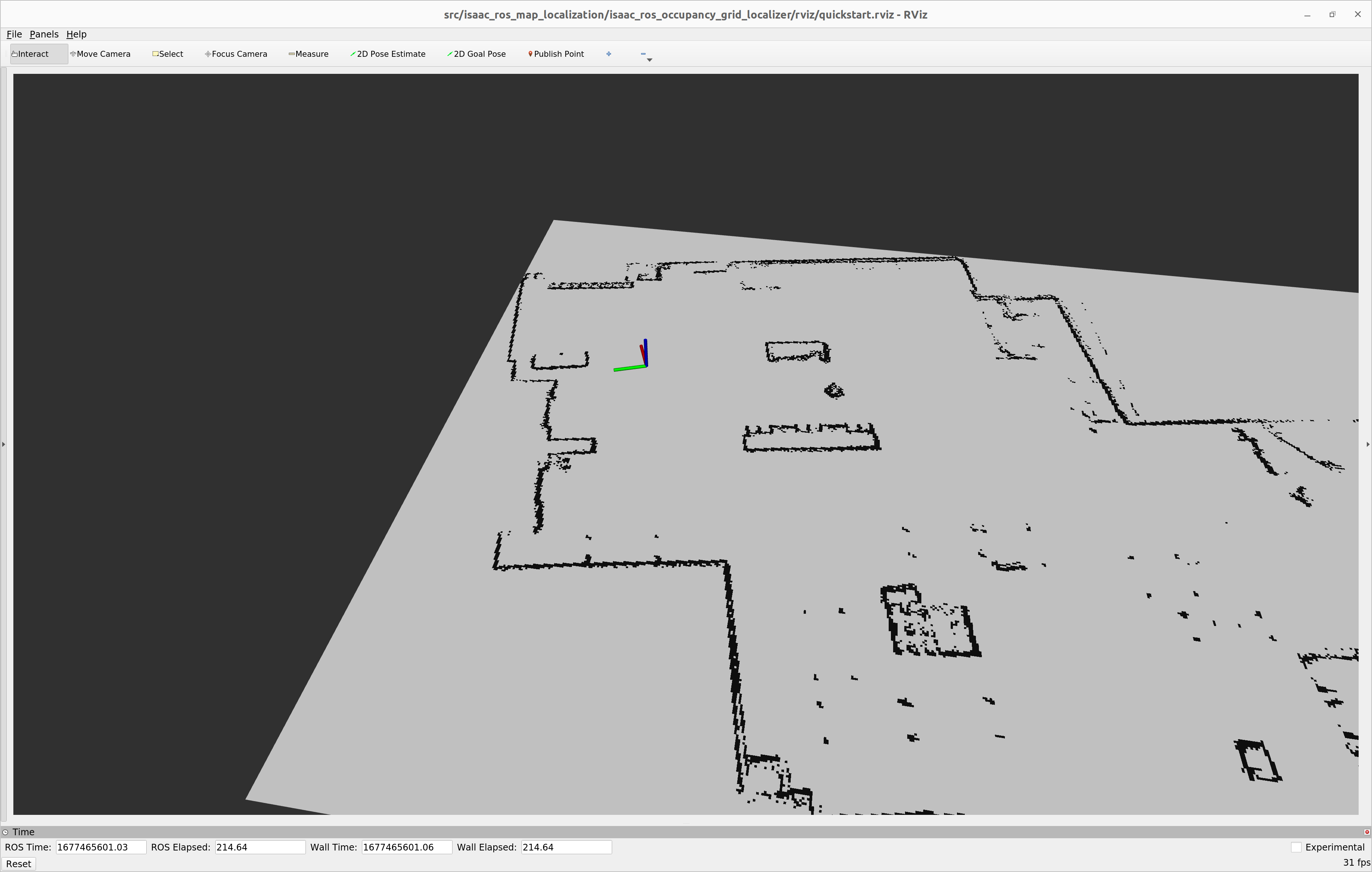
- Verify that you see a frame being generated in the map showing the
position of the LIDAR.
Try More Examples
To continue your exploration, check out the following suggested examples:
Troubleshooting
Isaac ROS Troubleshooting
For solutions to problems with Isaac ROS, see here.
API
Usage
ros2 launch isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer.launch.py
Note
Use the flatscan topic with the
trigger_grid_search_localization service to trigger localization
using a service.
Or publish directly to the flatscan_localization topic to
trigger localization every time a FlatScan message is received on
this topic.
Do not publish FlatScan messages to both flatscan and
flatscan_localization topics.
OccupancyGridLocalizerNode
ROS Parameters
Note
The ROS parameter names are the same as the Nav2
map_server
YAML parameters. This allows to load and pass the same YAML file to both Nav2 and
isaac_ros_occupancy_grid_localizer as shown in the
Isaac Sim Launch File
ROS Parameter |
Type |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
frame_id of localization result |
|
|
|
The meters per pixel of the |
|
|
|
The origin of the map loaded. Used to transform the output to compensate for the same transform made to the PNG file loaded by the Nav2 map_server. |
|
|
|
Pixels with occupancy probability greater than this threshold are considered completely occupied. This parameter is loaded from the the map YAML file. Supported values: |
|
|
|
Name of the PNG file used to load map. This should be in the same directory as the map YAML file specified in |
|
|
|
Absolute path to the map YAML file. From which we load the |
|
|
|
Maximum number of points in FlatScan Message that can be received used to pre-allocate GPU memory. |
|
|
|
The radius of the robot. This parameter is used to exclude poses which are too close to an obstacle.memory. |
|
|
|
The minimal output error used to normalize and compute confidence, if output error from best sample smaller or equal to this, the confidence is 1 |
|
|
|
The max output error from our best sample, if output error larger than this threshold, we conclude localization failed |
|
|
|
The maximum beam error used when comparing range scans. |
|
|
|
The GPU accelerated scan-and-match function can only handle a certain number of beams per range scan. The allowed values are {32, 64, 128, 256, 512}. If the number of beams in the range scan does not match this number a subset of beams will be taken. |
|
|
|
This is the number of scans to collect into a batch for the GPU kernel. Choose a value which matches your GPU well. |
|
|
|
Distance between sample points in meters. The smaller this number, the more sample poses will be considered. This leads to a higher accuracy and lower performance. |
|
|
|
Points range larger than this threshold will be marked as out of range and not used. |
|
|
|
Points range smaller than this threshold will be marked as invalid and not used. |
|
|
|
Minimal required scan FoV to run the localizer. |
|
|
|
Whether or not pick the closest angle beam in angle bucket, if not pick the average within an angular bucket |
ROS Topics Subscribed
ROS Topic |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
The input FlatScan messages buffer. The last message on this topic will be used as input for localization when the |
|
|
The topic to trigger localization directly without a buffer. Localization will be triggered every time a FlatScan message is received on this topic. |
ROS Topic |
Interface |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Pose of the scan data with respect to the map origin, as specified in the first note in the overview section |
ROS Services Advertised
ROS Service |
Interface |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
The service to trigger the global localization using the last scan received on the |