isaac_ros_correlated_timestamp_driver
Source code on GitHub.
Overview
An autonomous robotics system needs to perceive itself, its environment, and plan its actions to achieve a task, and control those actions, in a closed loop. Perception is provided by a combination of sensors, for example camera, LIDAR, IMU, touch, motor positions, wheel ticks, and others. Each of these sensors operate independently running at different frequencies and many on their own clocks. This is a challenge when more than one sensor is needed to reconstruct an understanding of the environment for planning of actions.
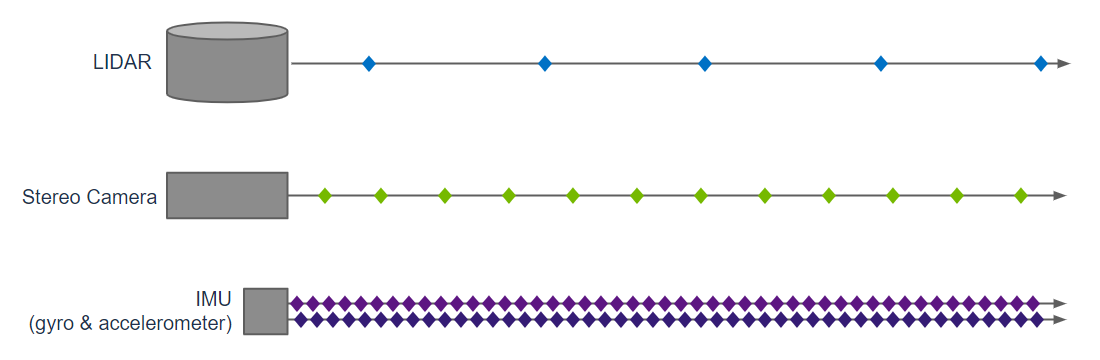
Example of 10hz LIDAR, 30Hz camera, and 100hz IMU sensors operating concurrently.
A common practice is to use the system time as the clock on which all sensor data is tracked in a single timeline. When the sensor’s data is received, an interrupt occurs causing the software to record the sensor acquisition time as the current system time. This lacks accuracy as the current system time does not account for time spent transmitting the sensor data to the processor, or kernel delays in servicing the interrupt which records the system time. The acquisition time of the sensor data will be both late, and subject to jitter. For some applications this lack of accuracy in the single timeline for sensor data is a problem for a precise reconstruction of the environment and precise planning at higher action speeds.
The isaac_ros_correlated_timestamp_driver provides functionality for highly accurate acquisition time of sensor
data translated to the system time. This is needed for precise reconstruction of the environment such as 3D maps, cost
maps, and obstacle avoidance from multiple concurrent sensors. This enables high action speeds as multi-sensor perception
has 2x orders of magnitude lower jitter (from 1ms to <10us).
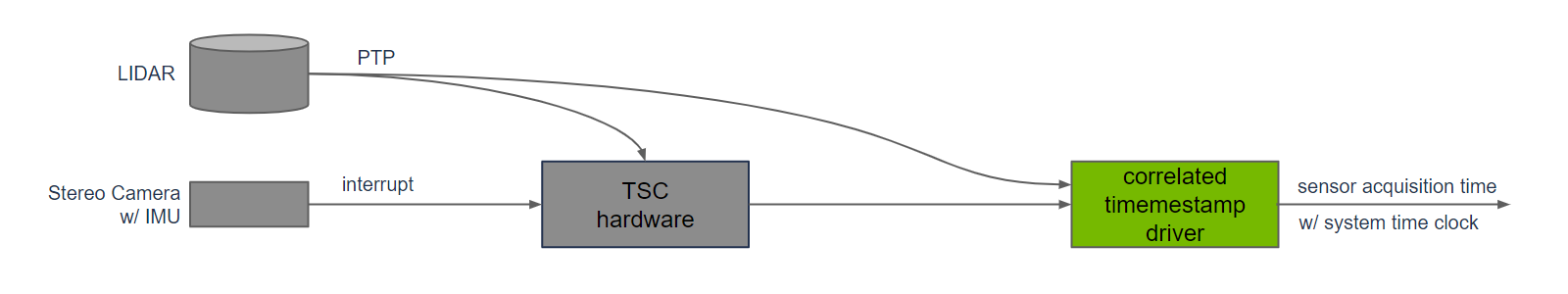
This accuracy is provided by isaac_ros_correlated_timemestamp_driver by leveraging hardware features in Jetson platforms.
A hardware feature uses TSC as the sensor acquisition time when an interrupt is received. This eliminates jitter in sensor
acquisition time measurements caused by delays in the kernel servicing interrupts. This is used for camera, and IMU data in Nova.
isaac_ros_correlated_timemestamp_driver converts TSC measurements to system time. In addition, time synchronization between
system time, and Ethernet is maintained with PTP, using phc2sys. Hardware provides time synchronization between TSC and PTP,
for highly precise sensor data acquisition times between camera and LIDAR sensors needed for sensor fusion in 3D reconstruction.
Quickstart
Set Up Development Environment
Set up your development environment by following the instructions in getting started.
Clone
isaac_ros_commonunder${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src.cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src && \ git clone -b release-3.2 https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_common.git isaac_ros_common
(Optional) Install dependencies for any sensors you want to use by following the sensor-specific guides.
Note
We strongly recommend installing all sensor dependencies before starting any quickstarts. Some sensor dependencies require restarting the Isaac ROS Dev container during installation, which will interrupt the quickstart process.
Build isaac_ros_correlated_timestamp_driver
Launch the Docker container using the
run_dev.shscript:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh
Install the prebuilt Debian package:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y ros-humble-isaac-ros-correlated-timestamp-driver
Clone this repository under
${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src && \ git clone -b release-3.2 https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_nova.git isaac_ros_nova
Launch the Docker container using the
run_dev.shscript:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh
Use
rosdepto install the package’s dependencies:sudo apt-get update
rosdep update && rosdep install --from-paths ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_nova/isaac_ros_correlated_timestamp_driver --ignore-src -y
Build the package from source:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS} && \ colcon build --symlink-install --packages-up-to isaac_ros_correlated_timestamp_driver
Source the ROS workspace:
Note
Make sure to repeat this step in every terminal created inside the Docker container.
Because this package was built from source, the enclosing workspace must be sourced for ROS to be able to find the package’s contents.
source install/setup.bash
Run Launch File
Continuing inside the Docker container, launch the correlated timestamp driver:
ros2 launch isaac_ros_correlated_timestamp_driver correlated_timestamp_driver.launch.py
Visualize Results
Open a new terminal inside the Docker container:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh
Output the timestamps:
ros2 topic echo /correlated_timestamp
Troubleshooting
Isaac ROS Troubleshooting
For solutions to problems with Isaac ROS, see troubleshooting.
API
Usage
ros2 launch isaac_ros_correlated_timestamp_driver correlated_timestamp_driver.launch.py target_container:=<Target Container> nvpps_dev_file:=<NVPPS Dev Name> use_time_since_epoch:=<Use Time Since Epoch>