Attention
As of June 30, 2025, the Isaac ROS Buildfarm for Isaac ROS 2.1 on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal is no longer supported.
Due to an isolated infrastructure event, all ROS 2 Humble Debian packages that were previously built for Ubuntu 20.04 are no longer available in the Isaac Apt Repository. All artifacts for Isaac ROS 3.0 and later are built and maintained with a more robust pipeline.
Users are encouraged to migrate to the latest version of Isaac ROS. The source code for Isaac ROS 2.1
continues to be available on the release-2.1 branches of the Isaac ROS
GitHub repositories.
The original documentation for Isaac ROS 2.1 is preserved below.
Tutorial for DNN Image Segmentation with NITROS Bridge
Overview
This tutorial walks you through how to run the isaac_ros_unet on ROS 2 Humble, while playing rosbag and getting the results from ROS Noetic through isaac_ros_nitros_bridge.
The tutorial is based on the ROS1 Bridge documentation.
Note
ROS actions are not supported by the ROS1 Bridge
Steps
Note
The ROS Noetic environment requires more storage space than the usual Isaac ROS Dev Docker-based development environment. We recommend at least 60 GB, to account for the size of the ROS Noetic container and datasets.
On Jetson platforms, NVMe SSD storage is required for sufficient and fast storage. See here
Set up your development environment by following the instructions here.
Clone the
isaac_ros_nitros_bridgerepository and its dependencies under Isaac ROS workspace:mkdir -p $ISAAC_ROS_WS/src && cd $ISAAC_ROS_WS/src && \ git clone https://github.com/ros2/ros1_bridge && \ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_common.git && \ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_nitros.git && \ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_nitros_bridge.git
Create a ROS 1 workspace for experimenting with Isaac ROS:
mkdir -p ${HOME}/workspaces/isaac_ros_1-dev/src echo "export ISAAC_ROS_1_WS=${HOME}/workspaces/isaac_ros_1-dev/" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
Note
Note that we are going to use the ISAAC_ROS_1_WS environmental variable in the future to refer to this ROS 1 workspace directory.
Clone the
isaac_ros_noetic_interfacesandisaac_ros_nitros_bridgerepositories into theisaac_ros_1-devdirectory:cd $ISAAC_ROS_1_WS/src && \ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_noetic_interfaces.git && \ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_nitros_bridge.git
Configure the container created by
isaac_ros_common/scripts/run_dev.shto includeros1_noetic. Create the.isaac_ros_common-configfile in theisaac_ros_common/scriptsdirectory:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common/scripts && \ touch .isaac_ros_common-config && \ echo CONFIG_IMAGE_KEY=ros2_humble.ros1_noetic >> .isaac_ros_common-config && \ echo "CONFIG_DOCKER_SEARCH_DIRS=(../../isaac_ros_nitros_bridge/docker)" >> .isaac_ros_common-config
Remove the following two lines from workspace-entrypoint.sh in the
isaac_ros_common/docker/scriptsdirectory becauseros1_bridgerequires a specificsetup.bashscript sourcing order:echo "source /opt/ros/${ROS_DISTRO}/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc source /opt/ros/${ROS_DISTRO}/setup.bash
Launch the Docker container:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh ${HOME}/workspaces
Build the custom ROS 1 packages and the ROS 2 packages. But do NOT build the
ros1_bridgepackage:source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash && \ cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros_1-dev && \ catkin_make_isolated --install --ignore-pkg isaac_ros_nitros_bridge_ros2 && \ source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash && \ cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros-dev && \ colcon build --symlink-install --packages-skip ros1_bridge
Note
You will see the following warning messages while building under ROS 2 Humble. This is expected as isaac_ros_nitros_bridge_ros1 and isaac_ros_ros1_forward are ROS Noetic packages and they are skipped from the building. Please ignore those warnings.
WARNING:colcon.colcon_cmake.task.cmake.build:Could not run installation step for package 'isaac_ros_nitros_bridge_ros1' because it has no 'install' target WARNING:colcon.colcon_cmake.task.cmake.build:Could not run installation step for package 'isaac_ros_ros1_forward' because it has no 'install' target
Attach a second terminal to the container:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh ${HOME}/workspaces
Note
Do NOT close the first terminal when you attach this second terminal to the container.
In the second terminal, build
ros1_bridgeand source the workspace:source isaac_ros_1-dev/install_isolated/setup.bash && \ source isaac_ros-dev/install/setup.bash && \ cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros-dev && \ colcon build --symlink-install --packages-select ros1_bridge --cmake-force-configure && \ source install/setup.bash
Now, we can setup isaac_ros_unet and run it with isaac_ros_nitros_bridge.
Clone
isaac_ros_unetand its dependencies under/workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros-dev/src:cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros-dev/src && \ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_image_segmentation.git && \ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_dnn_inference.git && \ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_image_pipeline.git
Complete isaac_ros_unet Quickstart step 5-6 to download image segmentation models and convert it to TensorRT engine.
Create a file called
/tmp/models/peoplesemsegnet_shuffleseg/config.pbtxtby copying the sample Triton config file:cp /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros-dev/src/isaac_ros_image_segmentation/resources/peoplesemsegnet_shuffleseg_config.pbtxt /tmp/models/peoplesemsegnet_shuffleseg/config.pbtxt
Inside the container, build
isaac_ros_unetand source the workspace:cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros-dev && \ colcon build --symlink-install --packages-up-to isaac_ros_unet && \ source install/setup.bash
Run the following launch files to spin up a demo of this package:
ros2 launch isaac_ros_unet isaac_ros_unet_triton.launch.py model_name:=peoplesemsegnet_shuffleseg model_repository_paths:=['/tmp/models'] input_binding_names:=['input_2:0'] output_binding_names:=['argmax_1'] network_output_type:='argmax' input_image_width:=1200 input_image_height:=632
Attach a fourth terminal to the Docker container:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh ${HOME}/workspaces
Launch the image converter launch file of
isaac_ros_nitros_bridge:cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros-dev && \ source install/setup.bash && \ ros2 launch isaac_ros_nitros_bridge_ros2 isaac_ros_image_converter.launch.py ros1_ws_path:=/workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros_1-dev/ pub_image_name:=image sub_image_name:=unet/colored_segmentation_mask
Attach a fourth terminal to the Docker container:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh ${HOME}/workspaces
Pull down a rosbag of image segmentation sample:
cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros_1-dev/src/isaac_ros_nitros_bridge && \ git lfs pull -X "" -I "resources/unet_sample_data_ros1.bag"
Play the rosbag under ROS Noetic:
cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev/isaac_ros_1-dev/ && \ source install_isolated/setup.bash && \ rosbag play -l "src/isaac_ros_nitros_bridge/resources/unet_sample_data_ros1.bag"
Attach a fifth terminal to the Docker container:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh ${HOME}/workspaces
Source
ros_noetic, downloadrvizfor ROS Noetic:source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash && \ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-rviz
Run
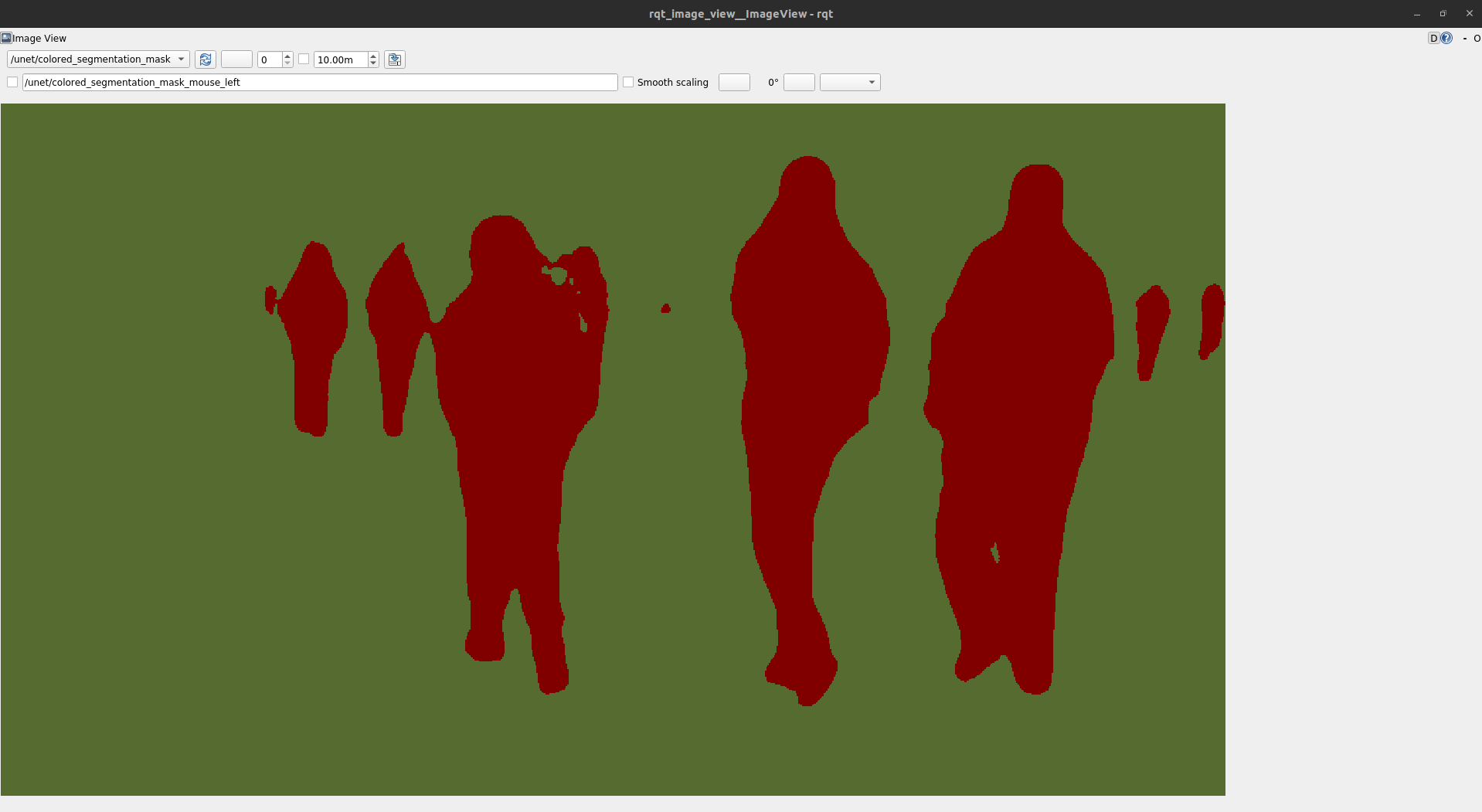
rvizunder ROS Noetic, add the colorized segmentation topic/ros1_output_imagesent from ROS 2 humble and visualize:rviz
You should be able to see the colorized segmentation: