Attention
As of June 30, 2025, the Isaac ROS Buildfarm for Isaac ROS 2.1 on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal is no longer supported.
Due to an isolated infrastructure event, all ROS 2 Humble Debian packages that were previously built for Ubuntu 20.04 are no longer available in the Isaac Apt Repository. All artifacts for Isaac ROS 3.0 and later are built and maintained with a more robust pipeline.
Users are encouraged to migrate to the latest version of Isaac ROS. The source code for Isaac ROS 2.1
continues to be available on the release-2.1 branches of the Isaac ROS
GitHub repositories.
The original documentation for Isaac ROS 2.1 is preserved below.
Tutorial for Freespace Segmentation using a ZED Camera
Overview
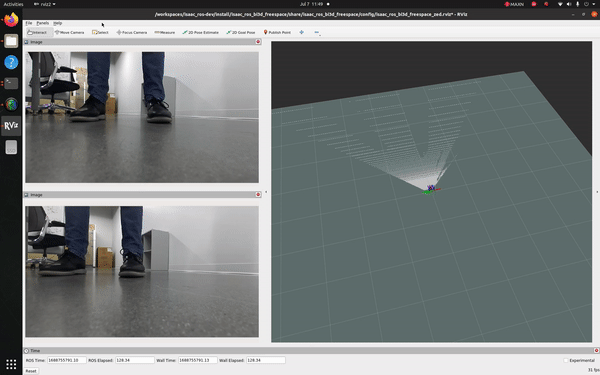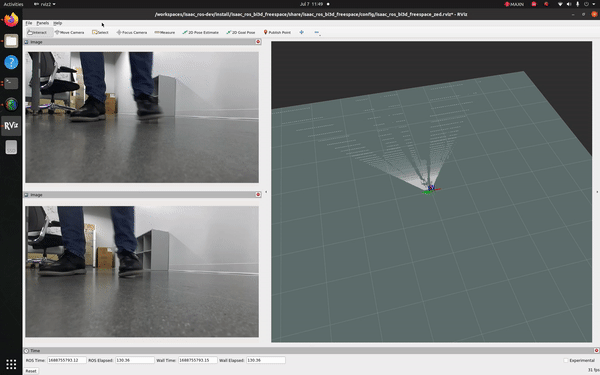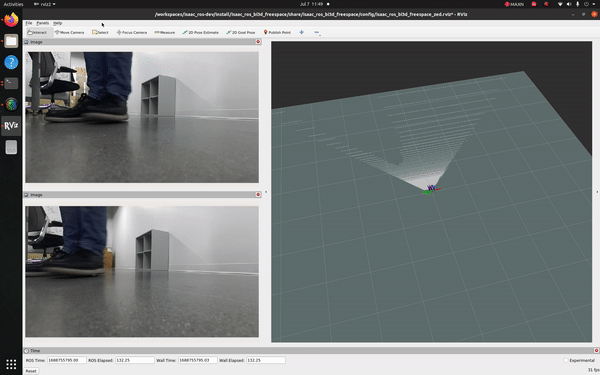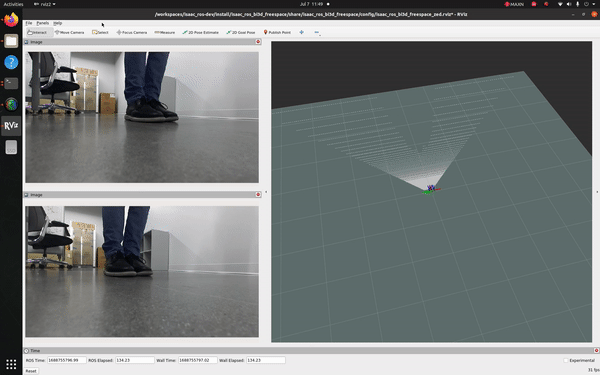
This tutorial demonstrates how to use a ZED camera and isaac_ros_bi3d_freespace to create a local occupancy grid.
Note
This tutorial requires a compatible ZED camera from the list of available cameras.
Tutorial Walkthrough
Complete the ZED setup tutorial.
Complete steps 1-7 described in the Freespace Quickstart.
Open a new terminal and launch the Docker container using the
run_dev.shscript:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh
Build and source the workspace:
cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev && \ colcon build --symlink-install && \ source install/setup.bash
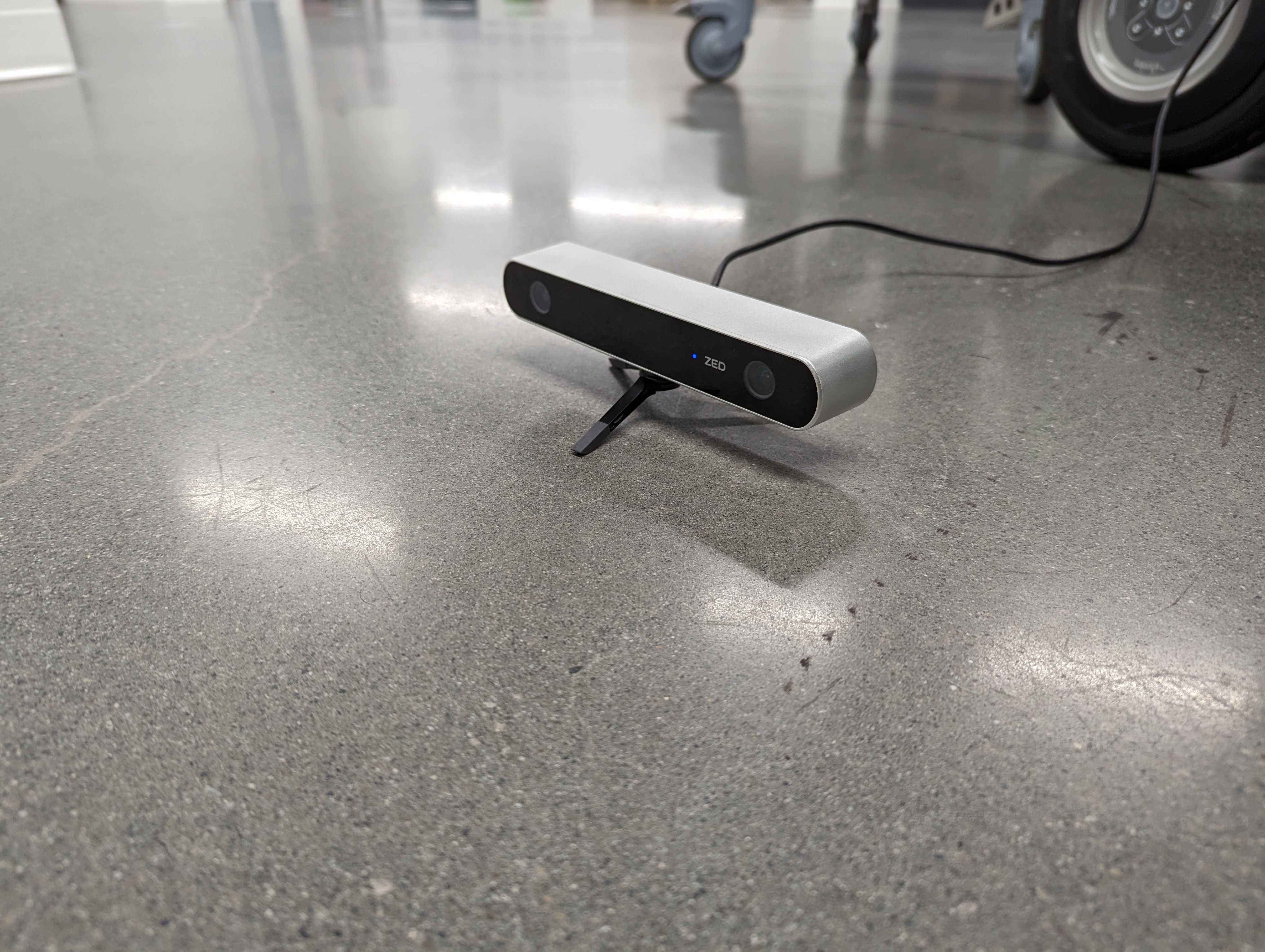
Set your camera as shown in the image below, which is on a tripod ~5cm tall and parallel to the ground. Or you can change the static transform in the launch file here, according to the placement of your camera with respect to an occupancy grid origin frame.

Note: If you are not using the ZED2i camera, modify the
camera_modelvariable in the launch file tozed,zed2,zed2i,zedm,zedx, orzedxm.Run the launch file, to launch the example:
ros2 launch isaac_ros_bi3d_freespace isaac_ros_bi3d_freespace_zed.launch.py featnet_engine_file_path:=/tmp/models/bi3d/bi3dnet_featnet.plan \ segnet_engine_file_path:=/tmp/models/bi3d/bi3dnet_segnet.plan \ max_disparity_values:=16
You should see an output similar to the one shown at the top of this page.