isaac_ros_yolov8#
Source code available on GitHub.
Quickstart#
Set Up Development Environment#
Set up your development environment by following the instructions in getting started.
(Optional) Install dependencies for any sensors you want to use by following the sensor-specific guides.
Note
We strongly recommend installing all sensor dependencies before starting any quickstarts. Some sensor dependencies require restarting the development environment during installation, which will interrupt the quickstart process.
Download Quickstart Assets#
Download quickstart data from NGC:
Make sure required libraries are installed.
sudo apt-get install -y curl jq tar
Then, run these commands to download the asset from NGC:
NGC_ORG="nvidia" NGC_TEAM="isaac" PACKAGE_NAME="isaac_ros_yolov8" NGC_RESOURCE="isaac_ros_yolov8_assets" NGC_FILENAME="quickstart.tar.gz" MAJOR_VERSION=4 MINOR_VERSION=0 VERSION_REQ_URL="https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/api/resources/versions?orgName=$NGC_ORG&teamName=$NGC_TEAM&name=$NGC_RESOURCE&isPublic=true&pageNumber=0&pageSize=100&sortOrder=CREATED_DATE_DESC" AVAILABLE_VERSIONS=$(curl -s \ -H "Accept: application/json" "$VERSION_REQ_URL") LATEST_VERSION_ID=$(echo $AVAILABLE_VERSIONS | jq -r " .recipeVersions[] | .versionId as \$v | \$v | select(test(\"^\\\\d+\\\\.\\\\d+\\\\.\\\\d+$\")) | split(\".\") | {major: .[0]|tonumber, minor: .[1]|tonumber, patch: .[2]|tonumber} | select(.major == $MAJOR_VERSION and .minor <= $MINOR_VERSION) | \$v " | sort -V | tail -n 1 ) if [ -z "$LATEST_VERSION_ID" ]; then echo "No corresponding version found for Isaac ROS $MAJOR_VERSION.$MINOR_VERSION" echo "Found versions:" echo $AVAILABLE_VERSIONS | jq -r '.recipeVersions[].versionId' else mkdir -p ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets && \ FILE_REQ_URL="https://api.ngc.nvidia.com/v2/resources/$NGC_ORG/$NGC_TEAM/$NGC_RESOURCE/\ versions/$LATEST_VERSION_ID/files/$NGC_FILENAME" && \ curl -LO --request GET "${FILE_REQ_URL}" && \ tar -xf ${NGC_FILENAME} -C ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets && \ rm ${NGC_FILENAME} fi
Download the model of your choice from Ultralytics YOLOv8. For this example, we use YOLOv8s.
cd Downloads && \ wget https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v0.0.0/yolov8s.pt
Convert the PyTorch model (
.pt) to a general ONNX model (.onnx). Export to ONNX following instructions given below or here. Then, convert the ONNX model to a TensorRT engine file (.plan) using trtexec. Arguments can be specified for FP16 quantization during this step. You may use either model for inference. You can use netron to visualize the ONNX model and note input and output names and dimensions.This can be done by first installing
ultralyticsandonnxvia pip:pip3 install --break-system-packages ultralytics pip3 install --break-system-packages onnx
Afterwards, convert the model from a
.ptfile to a.onnxmodel usingultralytics. This can be done by running:python3
Then within
python3, export the model to.onnxformat:>> from ultralytics import YOLO >> model = YOLO('yolov8s.pt') >> model.export(format='onnx')
Exit the interactive python shell, now convert the ONNX model to a TensorRT engine file using trtexec.
/usr/src/tensorrt/bin/trtexec --onnx=yolov8s.onnx --saveEngine=yolov8s.plan
Copy the generated
.onnxand.planmodel into the designated location for Isaac ROS (${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/models/yolov8):mkdir -p ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/models/yolov8 cp yolov8s.onnx ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/models/yolov8 cp yolov8s.plan ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/models/yolov8
Build isaac_ros_yolov8#
Activate the Isaac ROS environment:
isaac-ros activateInstall the prebuilt Debian package:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y ros-jazzy-isaac-ros-yolov8 ros-jazzy-isaac-ros-dnn-image-encoder ros-jazzy-isaac-ros-tensor-rt
Install Git LFS:
sudo apt-get install -y git-lfs && git lfs install
Clone this repository under
${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src:cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src && \ git clone -b release-4.0 https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_object_detection.git isaac_ros_object_detection
Activate the Isaac ROS environment:
isaac-ros activateUse
rosdepto install the package’s dependencies:sudo apt-get update
rosdep update && rosdep install --from-paths ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_object_detection/isaac_ros_yolov8 --ignore-src -y
Build the package from source:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS} && \ colcon build --symlink-install --packages-up-to isaac_ros_yolov8 --base-paths ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_object_detection/isaac_ros_yolov8
Source the ROS workspace:
Note
Make sure to repeat this step in every terminal created inside the Isaac ROS environment.
Since this package was built from source, the enclosing workspace must be sourced for ROS to be able to find the package’s contents.
source install/setup.bash
Run Launch File#
Continuing inside the Isaac ROS environment, install the following dependencies:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y ros-jazzy-isaac-ros-examples
Run the following launch file to spin up a demo of this package using the quickstart rosbag:
cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev && \ ros2 launch isaac_ros_examples isaac_ros_examples.launch.py launch_fragments:=yolov8 interface_specs_file:=${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/isaac_ros_yolov8/quickstart_interface_specs.json \ engine_file_path:=${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/models/yolov8/yolov8s.plan
Open a second terminal inside the Isaac ROS environment:
isaac-ros activateRun the rosbag file to simulate an image stream:
ros2 bag play -l ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/isaac_ros_yolov8/quickstart.bag
Ensure that you have already set up your RealSense camera using the RealSense setup tutorial. If you have not, please set up the sensor and then restart this quickstart from the beginning.
Continuing inside the Isaac ROS environment, install the following dependencies:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y ros-jazzy-isaac-ros-examples ros-jazzy-isaac-ros-realsense
Run the following launch file to spin up a demo of this package using a RealSense camera:
ros2 launch isaac_ros_examples isaac_ros_examples.launch.py launch_fragments:=realsense_mono_rect,yolov8 \ engine_file_path:=${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/models/yolov8/yolov8s.plan
Ensure that you have already set up your ZED camera using ZED setup tutorial.
Continuing inside the Isaac ROS environment, install dependencies:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y ros-jazzy-isaac-ros-examples ros-jazzy-isaac-ros-stereo-image-proc ros-jazzy-isaac-ros-zed
Run the following launch file to spin up a demo of this package using a ZED Camera:
ros2 launch isaac_ros_examples isaac_ros_examples.launch.py \ launch_fragments:=zed_mono_rect,yolov8 \ engine_file_path:=${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/models/yolov8/yolov8s.plan \ interface_specs_file:=${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/isaac_ros_yolov8/zed2_quickstart_interface_specs.json
Note
If you are using the ZED X series, replace zed2_quickstart_interface_specs.json with zedx_quickstart_interface_specs.json in the above command.
Visualize Results#
Open a new terminal inside the Isaac ROS environment:
isaac-ros activateRun the YOLOv8 visualization script:
ros2 run isaac_ros_yolov8 isaac_ros_yolov8_visualizer.py
Open another terminal inside the Isaac ROS environment:
isaac-ros activateVisualize and validate the output of the package with
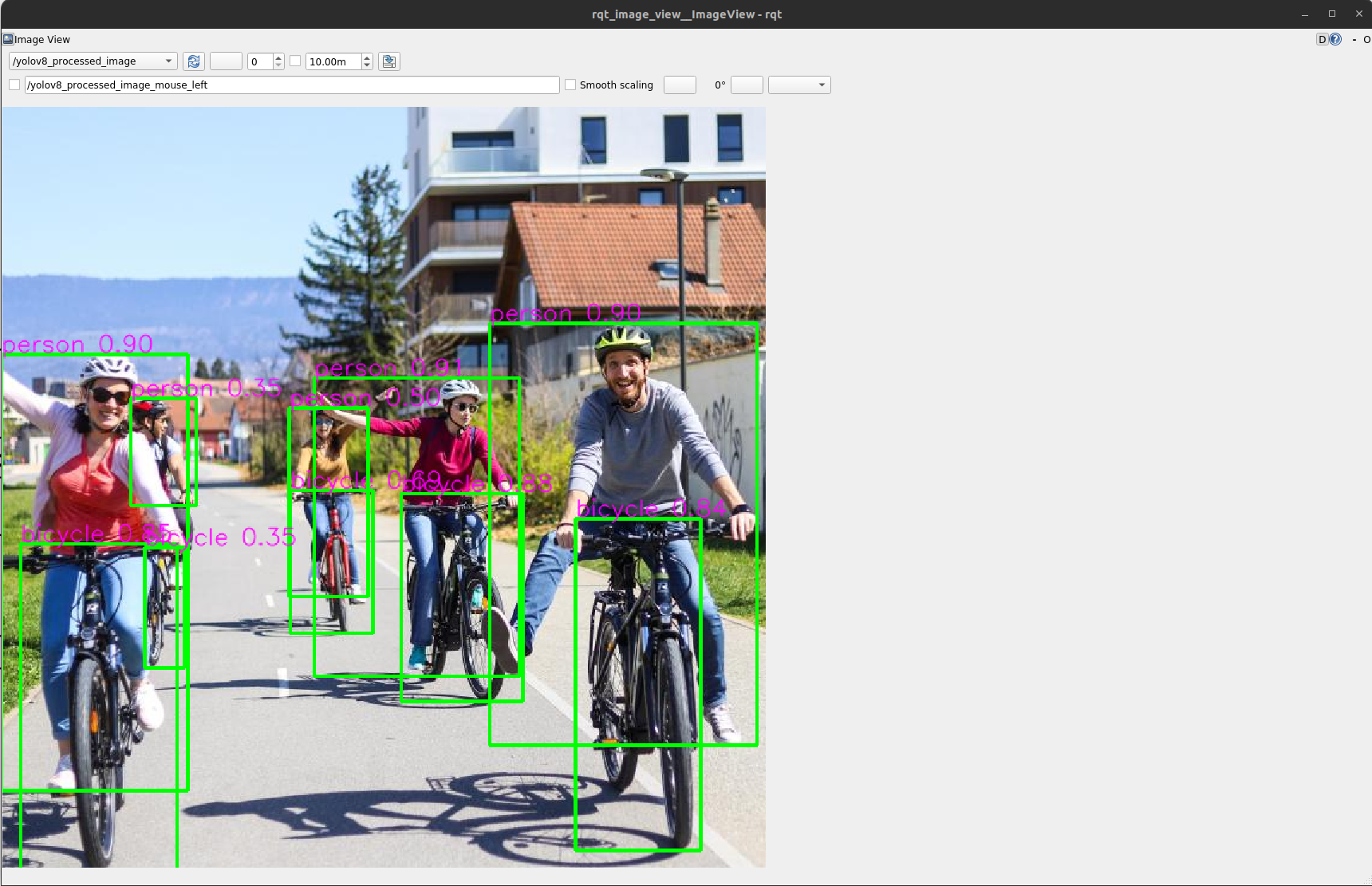
rqt_image_view:ros2 run rqt_image_view rqt_image_view /yolov8_processed_image
Your output should look like this:
Troubleshooting#
Isaac ROS Troubleshooting#
For solutions to problems with Isaac ROS, please check here.
Deep Learning Troubleshooting#
For solutions to problems with using DNN models, please check here.
API#
Usage#
ros2 launch isaac_ros_yolov8 isaac_ros_yolov8_visualize.launch.py model_file_path:=<model_file_path> engine_file_path:=<engine_file_path> input_binding_names:=<input_binding_names> output_binding_names:=<output_binding_names> network_image_width:=<network_image_width> network_image_height:=<network_image_height> force_engine_update:=<force_engine_update> image_mean:=<image_mean> image_stddev:=<image_stddev> confidence_threshold:=<confidence_threshold> nms_threshold:=<nms_threshold>
Yolov8DecoderNode#
ROS Parameters#
ROS Parameter |
Type |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Name of the inferred output tensor published by the Managed NITROS Publisher. The decoder uses this name to get the output tensor. |
|
|
|
Detection confidence threshold. Used to filter candidate detections during Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). |
|
|
|
NMS IOU threshold. |
ROS Topics Subscribed#
ROS Topic |
Interface |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Tensor list from the managed NITROS subscriber that represents the inferred aligned bounding boxes. |
ROS Topics Published#
ROS Topic |
Interface |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Aligned image bounding boxes with detection class. |