Multi-RealSense Camera Examples#
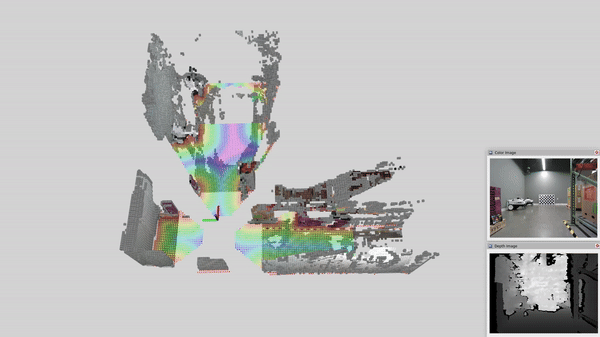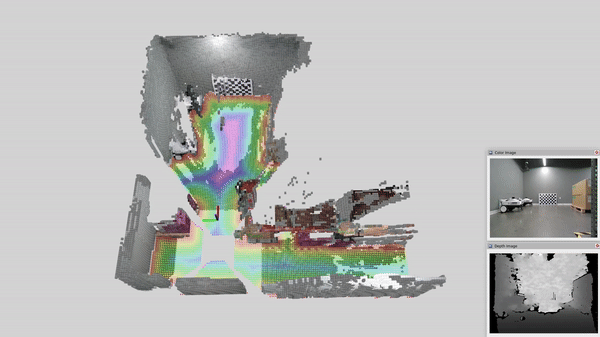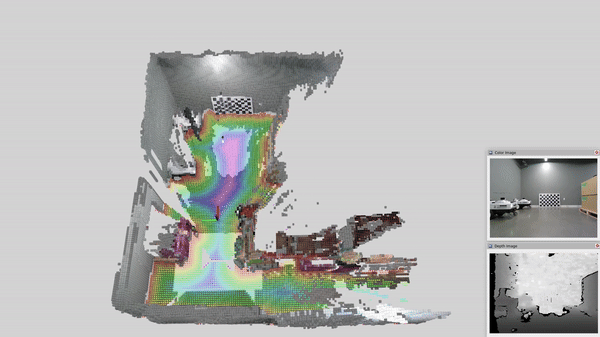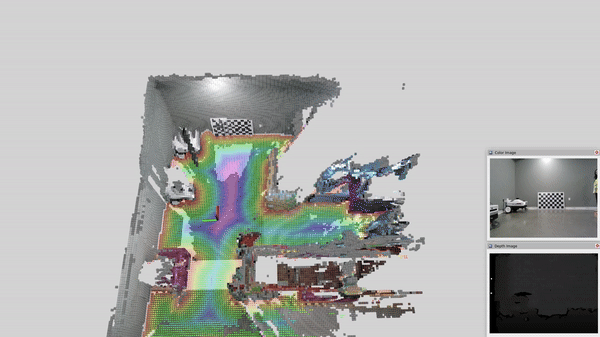
This page contains tutorials for running nvblox with multiple RealSense cameras.
Install#
Complete the installation instructions from the single RealSense tutorial.
Multi-RealSense Camera Setup#
Activate the Isaac ROS environment (if not started in the install step)
isaac-ros activateFor each RealSense camera, plug in one RealSense and unplug all other RealSense cameras.
rs-enumerate-devices
Up top it will list the device type, Serial Number, and Firmware Version. Write down the Serial Number for this RealSense. Example:
Device info: Name : Intel RealSense D455 Serial Number : 151422250659 Firmware Version : 5.16.0.1
3. Add a calibration URDF file to specify the transformation between base_link and each RealSense camera.
The calibration example file is stored in a default location
URDF file.
Nvblox will use it without requiring any additional arguments. Alternatively, you could create a
camera calibration URDF file, which can then be passed with multicam_urdf_path as,
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ multicam_urdf_path:=<"urdf_nominals_file_path">
RealSense Example#
This example runs nvblox-based reconstruction from multiple RealSense cameras, either from live data coming directly off RealSense cameras, or from recorded data coming from a ROSbag.
Activate the Isaac ROS environment (if not started in the install step)
isaac-ros activateNavigate (inside the Isaac ROS environment) to the workspace folder, and source the workspace
cd /workspaces/isaac_ros-dev source install/setup.bash
Run the RealSense example, either live from cameras or from a recorded ROSbag.
Start cameras. Provide the serial numbers identified above as a list separated by comma (
camera_serial_numbers), and the number of cameras identified as an integer (num_cameras), for example:
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense.launch.py \ run_standalone:=True \ camera_serial_numbers:='211523062311,151223061441,151422251043,215122256933' \ container_name:='nvblox_container' \ num_cameras:=4
Switch to another terminal and start the Isaac ROS environment. For each camera (identified by the index of the camera
INDEX), ensure it publishing topics at expected frequency. 15Hz for color, and 60Hz for the first camera’s depth (identified by the order ofcamera_serial_numbersinput in the previous step), and 30Hz for other camera’s depth. Otherwise restart the cameras in the last step until they meet the expected rates.
ros2 topic hz /camera${INDEX}/color/image_raw ros2 topic hz /camera${INDEX}/depth/image_rect_raw
Switch to another terminal and start the Isaac ROS environment. Provide the number of cameras identified as an integer (
num_cameras) and launch nvblox as,
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ num_cameras:=4 \ mode:=static attach_to_container:=True \ container_name:='nvblox_container' \ run_realsense:=False
Use the rosbag
galileo_static_3_2from :nvblox quickstart or record your own bag.Provide the number of cameras identified as an integer (num_cameras), and launch nvblox thru rosbag replay:
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ num_cameras:=4 \ mode:=static \ attach_to_container:=False \ run_realsense:=False \ rosbag:=<YOUR_ROSBAG_PATH>
Note
If you want to restrict odometry to a 2D plane
(for example, to run a robot in a flat environment),
you can use the enable_ground_constraint_in_odometry argument.
Note
Based on how RealSense cameras are mounted to the platform and calibrated, users are expected to tune ESDF slice height specified in nvblox config file. Details about nvblox mapping parameters could be found at mapper parameters.
Warning
The RealSense camera emitter state might be invalid and the splitter will filter the opposite images to cuVSLAM and nvblox. This may lead to poor tracking and reconstruction. See the RealSense troubleshooting section for more details.
Recording Data with RealSense#
To record RealSense data for nvblox:
Connect the camera, activate the Isaac ROS environment and source the workspace as explained in RealSense Camera Examples.
Start the cameras. Provide the serial numbers identified above as a list separated by comma (
camera_serial_numbers), and the number of cameras identified as an integer (num_cameras`), for example:ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense.launch.py \ run_standalone:=True \ camera_serial_numbers:='211523062311,151223061441,151422251043,215122256933' \ container_name:='nvblox_container' \ num_cameras:=4
Switch to another terminal and start the Isaac ROS environment. For each camera (identified by the index of the camera
INDEX), ensure it publishing topics at expected frequency. 15Hz for color, and 60Hz for the first camera’s depth (identified by the order ofcamera_serial_numbersin the previous step), and 30Hz for other camera’s depth. Otherwise restart the cameras in the last step until they meet the expected rates.ros2 topic hz /camera${INDEX}/color/image_raw ros2 topic hz /camera${INDEX}/depth/image_rect_raw
Switch to another terminal and start the Isaac ROS environment. Provide the serial numbers identified above as a list separated by comma (
camera_serial_numbers), and the number of cameras identified as an integer (num_cameras`). Start recording as,ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup record_realsense.launch.py \ num_cameras:=4 \ camera_serial_numbers:='211523062311,151223061441,151422251043,215122256933' \ run_rqt:=False \ run_realsense:=False
Stop the recording and cameras when done.
The resulting ROSbag can be run using the instructions above.
Reconstruction With People Segmentation#
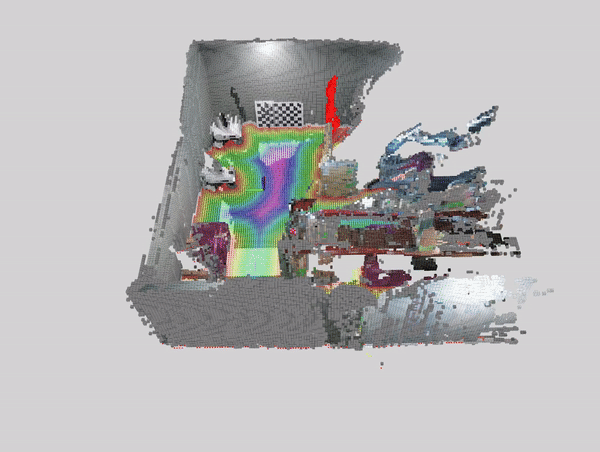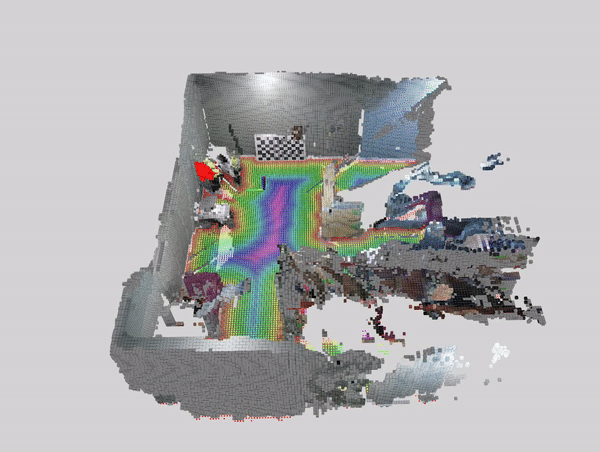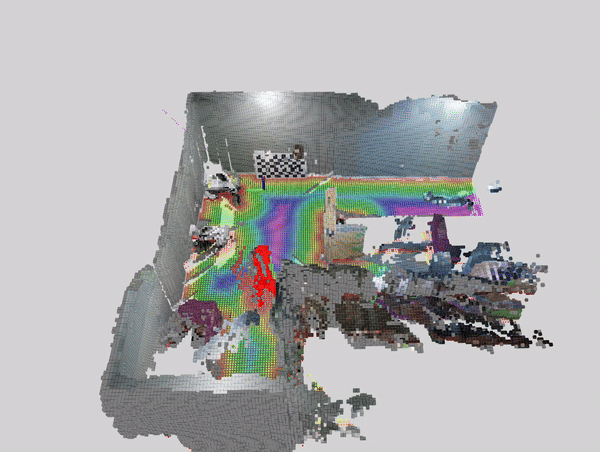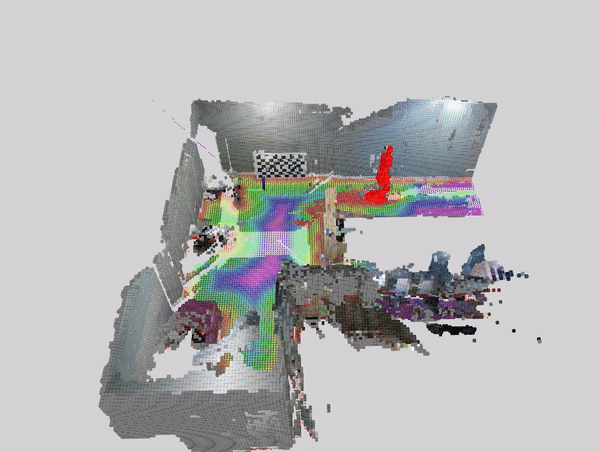
This tutorial demonstrates how to perform dynamic people reconstruction using people segmentation models for systems with multiple RealSense cameras. For more information see the single realsense tutorial.
Note
If you are on a desktop machine, we recommend using the
PeopleSemSegNet_Vanilla.
On Jetson platforms we recommend the lighter PeopleSemSegNet_ShuffleSeg
model that is provided in Isaac ROS Image Segmentation
for better segmentation performance.
Note
Provide the number of cameras identified as an integer (num_cameras) when launching nvblox as followings.
Download and install the segmentation models as described in the single RealSense with people segmentation example.
Multi-RealSense launch commands are provided below. Live from RealSense cameras assumes cameras are started successfully as instructions above.
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ mode:=people_segmentation \ num_cameras:=4 \ attach_to_container:=True \ container_name:='nvblox_container' \ run_realsense:=False
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ mode:=people_segmentation \ people_segmentation:=peoplesemsegnet_shuffleseg \ num_cameras:=4 \ attach_to_container:=True \ container_name:='nvblox_container' \ run_realsense:=False
Use the rosbag
galileo_people_3_2from :nvblox quickstart or record your own bag.Launch the rosbag:
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ mode:=people_segmentation \ rosbag:=<YOUR_ROSBAG_PATH> \ num_cameras:=4 \ attach_to_container:=False \ run_realsense:=False
Use the rosbag
galileo_people_3_2from :nvblox quickstart or record your own bag.Launch the rosbag:
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ mode:=people_segmentation \ people_segmentation:=peoplesemsegnet_shuffleseg \ rosbag:=<YOUR_ROSBAG_PATH> \ num_cameras:=4 \ attach_to_container:=False \ run_realsense:=False
Reconstruction With People Detection#
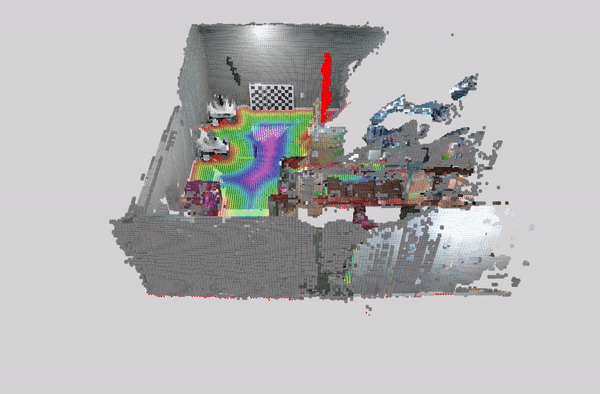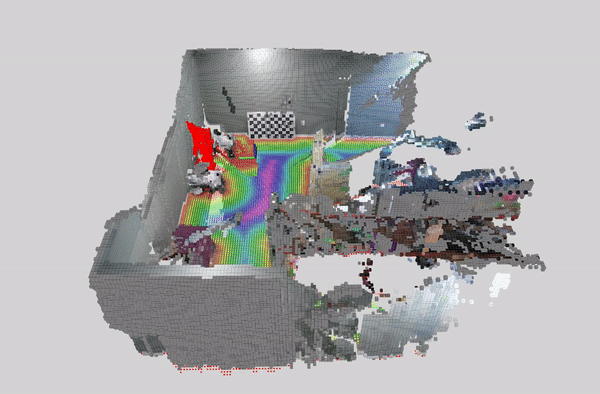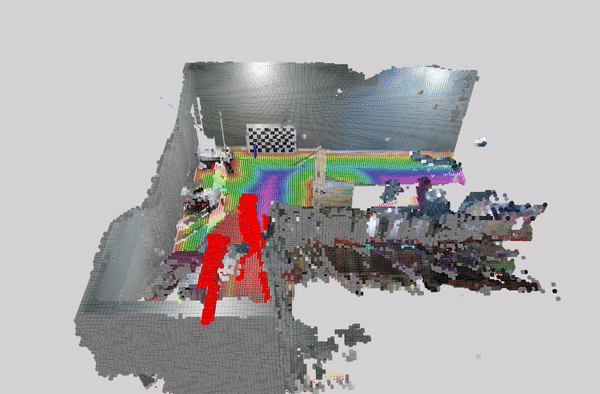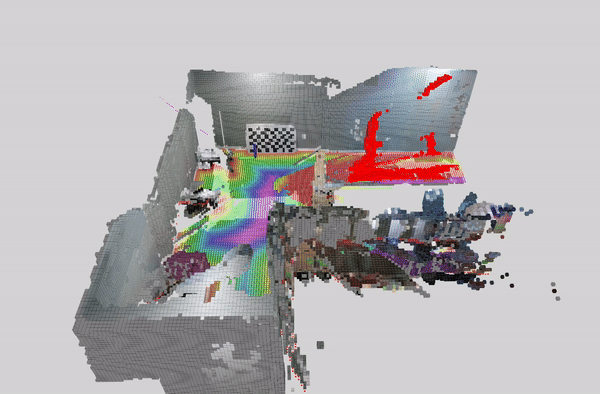
This tutorial demonstrates how to perform dynamic people reconstruction using a detection model for systems with multiple RealSense cameras. For more information see the single RealSense tutorial.
Note
Provide the number of cameras identified as an integer (num_cameras) when launching nvblox as followings.
Download and install the detection models as described in the single RealSense with people detection example.
Multi-RealSense launch commands are provided below. Live from RealSense cameras assumes cameras are started successfully as instructions above.
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ mode:=people_detection \ num_cameras:=4 \ attach_to_container:=True \ container_name:='nvblox_container' \ run_realsense:=False
Use the rosbag
galileo_people_3_2from :nvblox quickstart or record your own bag.Launch the rosbag:
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ mode:=people_detection \ rosbag:=<YOUR_ROSBAG_PATH> \ num_cameras:=4 \ attach_to_container:=False \ run_realsense:=False
Reconstruction With Dynamic Scene Elements#
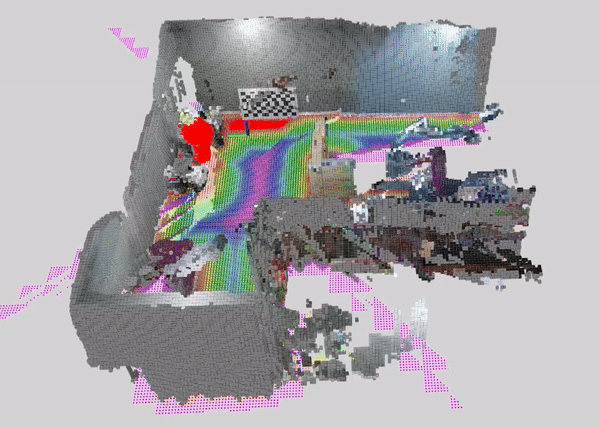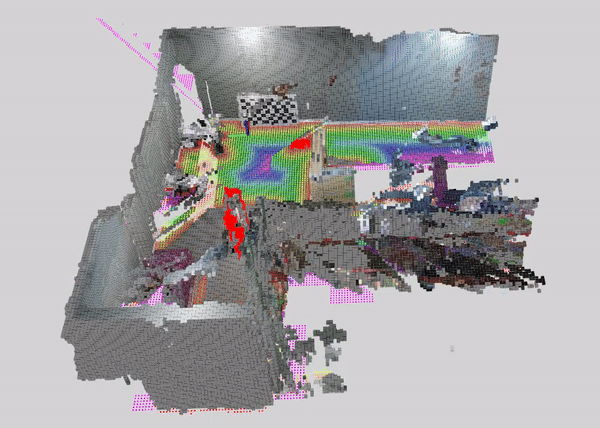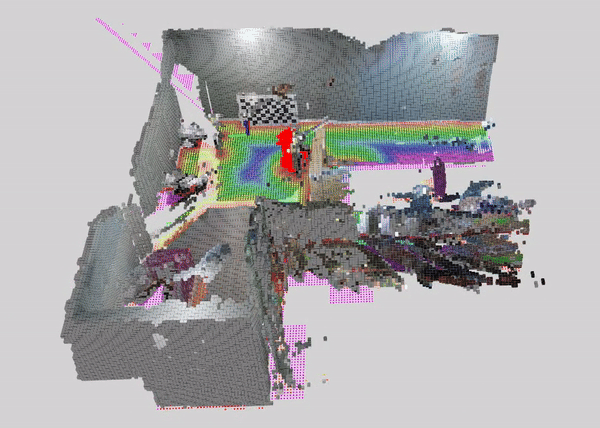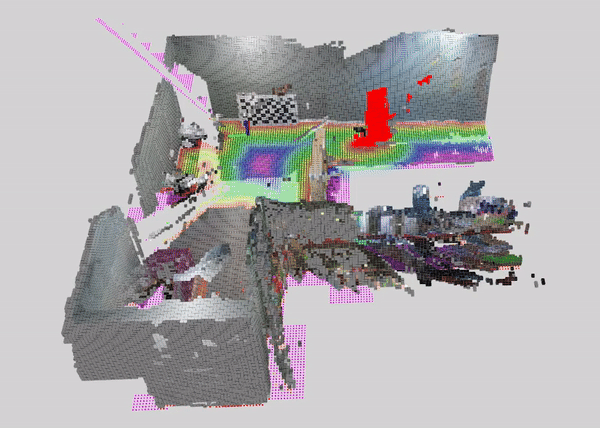
This tutorial demonstrates how to perform dynamic people reconstruction using a dynamic detection for systems with multiple RealSense cameras. For more information see the single RealSense tutorial.
Note
Provide the number of cameras identified as an integer (num_cameras) when launching nvblox as followings.
Multi-RealSense launch commands are provided below. Live from RealSense cameras assumes cameras are started successfully as instructions above.
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ mode:=dynamic \ num_cameras:=4 \ attach_to_container:=True \ container_name:='nvblox_container' \ run_realsense:=False
Use the rosbag
galileo_people_3_2from :nvblox quickstart or record your own bag.Launch the rosbag:
ros2 launch nvblox_examples_bringup realsense_example.launch.py \ mode:=dynamic \ rosbag:=<YOUR_ROSBAG_PATH> \ num_cameras:=4 \ attach_to_container:=False \ run_realsense:=False
Troubleshooting#
See RealSense Issues.